What Are Emergent Properties and How Do They Manifest?
In nature, science, and technology, emergent properties are fascinating phenomena. These qualities or behaviors arise when system components interact in complex ways. They produce outcomes that can’t be fully predicted by examining parts alone. Emergent properties are central to ecosystems, biological organisms, human consciousness, and artificial intelligence.
Understanding Emergent Properties
Emergence describes how collective phenomena arise from simpler interactions. Components follow basic rules or behaviors. Their collective dynamics create outcomes greater than the sum of their parts. This concept is key to understanding complexity in natural and artificial systems.
For example, a flock of birds follows simple rules like maintaining distance and aligning flight direction. The flock as a whole then exhibits sophisticated patterns and synchronized movements. This collective behavior is an emergent property.
Key Characteristics of Emergent Properties
- Unpredictability: The behavior or quality can’t be easily predicted by analyzing individual components alone.
- Non-linearity: Small changes in interactions can lead to large effects in the outcome.
- Dependence on Interactions: Emergent properties arise only when components interact.
- Scale Transition: They often manifest at a higher organizational level than the individual components.
Examples of Emergent Properties in Nature
- Biological Systems:
- The human brain’s neurons interact to give rise to consciousness, an emergent property still not fully understood.
- Ant colonies exhibit complex problem-solving and resource allocation without central control.
- Physical Systems:
- Water’s unique properties, like surface tension and flow, arise from molecular interactions.
- Hurricanes form from interactions between warm ocean water, air currents, and atmospheric pressure.
- Social and Economic Systems:
- Markets and economies emerge from countless individual transactions and decisions.
- Artificial Systems:
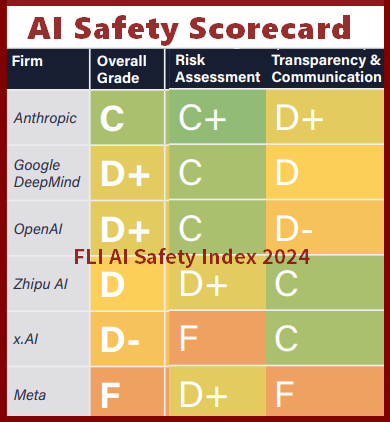
- In AI, emergent properties appear in neural networks. Well-trained AI models can generate coherent text, recognize faces, or play complex games.
How Do Emergent Properties Manifest?
- Local Interactions: Components follow simple rules, leading to complex patterns. For instance, fish swarming arises from local responses.
- Feedback Loops: Positive or negative feedback amplifies or stabilizes behaviors, leading to new organizational states.
- Self-Organization: Systems organize themselves without external control, like galaxy formation or snowflake structures.
- Critical Mass: Emergent behaviors appear once a system reaches a complexity threshold.
Why Are Emergent Properties Important?
Understanding emergent properties is vital for solving complex problems in science, technology, and society. By studying emergence, we can:
- Improve Predictions: Better understand systems like ecosystems, economies, and social networks.
- Optimize Systems: Design more efficient algorithms, technologies, and infrastructures.
- Advance Knowledge: Uncover fundamental principles about complexity and order in the universe.
Conclusion
Emergent properties showcase the beauty and intricacy of interconnected systems. They teach us that the whole is often more than the sum of its parts. Exploring emergence opens doors to deeper understanding and innovation, whether in unraveling brain mysteries, designing smarter AI, or fostering sustainable ecosystems.







Yeah